Xenos - X射线蒙特卡洛代码套件
Xenos软件套件是模拟X射线、电子及其相互作用的资源。组件作为耦合或独立应用程序用于电场和磁场计算、电子束设计、辐射传输的蒙特卡罗建模和热分析。
Xenos(X射线/电子数值优化套件)使一组2D/3D有限元程序,可模拟您想了解的有关X射线和电子的全部信息。组件程序计算电场、磁场、带电粒子动力学、材料中的电子-光子-正电子传输和热传输。Professional版在64位Windows机器上具有无限的内存访问和高效的并行处理功能。
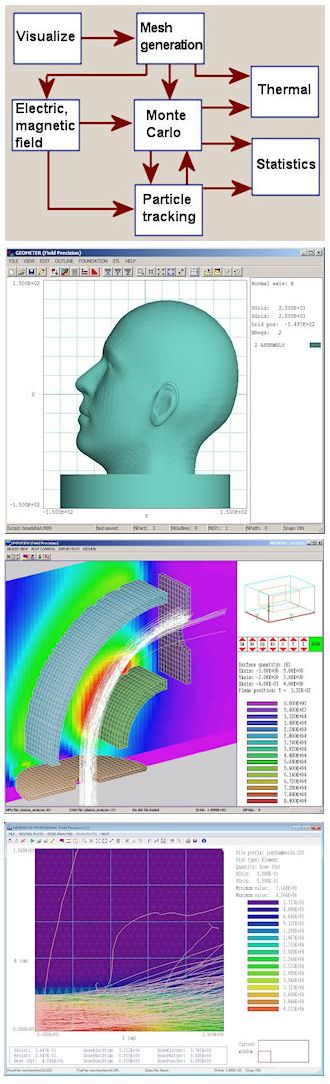
下图显示了程序如何作为一个集成系统进行通信。应用程序几何是在Geometer的交互式图形环境中定义的。MetaMesh使用这些信息为解决方案程序创建六面体元素的保形网格。相同或不同的网格可用于定义
1)用于电场计算(HiPhi)的电极和电介质
2)用于磁场计算(Magnum)的线圈、铁和永磁体
3)用于蒙特卡罗辐射传输的元素和化合物(GamBet)
4)用于热传输的固体材料(HeatWave)
从这一点来看,有几种选择:
-
GamBet可以从HiPhi和Magnum导入字段信息。在这种情况下,电子和正电子的历史受到洛伦兹力以及物质相互作用的影响。
-
GamBet可以将信息传输到OmniTrak以跟踪目标(即正电子束)中产生的粒子的轨道
-
来自HiPhi和Magnum的现场信息可以传输到OmniTrak以设计电子枪和传输系统。然后可以将生成的光束分布发送到GamBet以研究目标相互作用
-
GamBet记录了沉积功率密度的空间发布。HeatWave将这些信息用于静态和动态热模拟
-
GenDist对来自OmniTrak和GamBet的粒子分布进行统计分析
Xenos包含一组用于2D计算的并行程序。2D和3D程序之间的交互有多种途径。
可以使用Xenos执行的一些计算:
-
热离子阴极的加热器功率
-
具有多个电子或X射线束的临床剂量分布
-
高压穿通中的峰值电场
-
光束诊断校准
-
电子束焊机的屏蔽要求和温度曲线
-
由光子散射设置的X射线成像系统的分辨率限制
-
用于光束线的弯曲和聚焦磁铁的设计
-
光学系统中的正电子产生和捕获
-
螺线管或四极透镜中的像差
-
来自周围铁结构的光束扰动
-
高强度电子枪中的空间电荷限制电流
-
通过脉冲束加热X射线目标
-
用于高功率微波管的周期性永磁阵列
-
板束辐照器的3D设计
-
屏蔽MRI磁体
-
具有3D边缘场的磁或电偏转器中的数值准确电子轨道
【英文介绍】
The Xenos software suite is the ultimate resource to model X-rays, electrons and their interactions. Components function as coupled or stand-alone applications for electric and magnetic field calculations, electron beam design, Monte Carlo modeling of radiation transport and thermal analysis.
Xenos (X-ray/electron numerical optimization suite) is a set of advanced 2D/3D finite-element programs that simulates everything you'll want to know about X-rays and electrons. Component programs calculate electric fields, magnetic fields, charged-particle dynamics, electron-photon-positron transport in materials and thermal transport. The Professional version features unlimited memory access and efficient parallel processing on 64-bit Windows machines.
The application geometry is defined in the interactive graphical environment of Geometer. MetaMesh uses the information to create conformal meshes of hexahedron elements for the solution programs. The same or different meshes may be used to define 1) electrodes and dielectrics for electrical field calculations (HiPhi), 2) coils, iron and permanent magnets for magnetic field calculations (Magnum), 3) elements and compounds for Monte Carlo radiation transport (GamBet) and 4) solid materials for thermal transport (HeatWave). From this point, there are several options:
-
GamBet can import field information from HiPhi and Magnum. In this case, electron and positron histories are influenced by Lorentz forces as well as material interactions
-
GamBet can transfer information to OmniTrak to trace orbits of particles generated in a target (i.e., a positron beam)
-
Field information from HiPhi and Magnum can be transferred to OmniTrak to design electron guns and transport systems. The resulting beam distributions can then be sent to GamBet to study target interactions
-
GamBet records the spatial distribution of deposited power density. The information is used by HeatWave for static and dynamic thermal simulations
-
GenDist performs statistical analysis of particle distributions from OmniTrak and Gambet
Xenos includes a parallel set of programs for 2D calculations. There are several pathways for interactions between the 2D and 3D programs.
Some calculations you can perform with Xenos
-
Heater power for a thermionic cathode.
-
Clinical dose distributions with multiple electron or X-ray beams.
-
Peak electric field in a high-voltage feethrough.
-
Calibration of beam diagnostics.
-
Shielding requirements and temperature profiles for an electron-beam welder.
-
Resolution limits in an X-ray imaging system set by photon scattering.
-
Design of bending and focusing magnets for a beam line.
-
Positron production and capture in an optical system.
-
Aberrations in solenoid or quadrupole lenses.
-
Beam perturbations from surrounding iron structures.
-
Space-charge-limited current in high-perveance electron guns.
-
Heating of an X-ray target by a pulsed beam.
-
Periodic permanent-magnet arrays for high-power microwave tubes.
-
3D design of sheet-beam irradiators.
-
Shielding of MRI magnets.
-
Numerically-exact electron orbits in magnetic or electric deflectors with 3D edge fields.
- 2026-03-11
- 2026-03-11
- 2026-03-10
- 2026-02-09
- 2026-01-20
- 2026-01-16
- 2026-03-11
- 2026-03-11
- 2026-03-11
- 2026-03-11
- 2026-03-11
- 2026-03-11